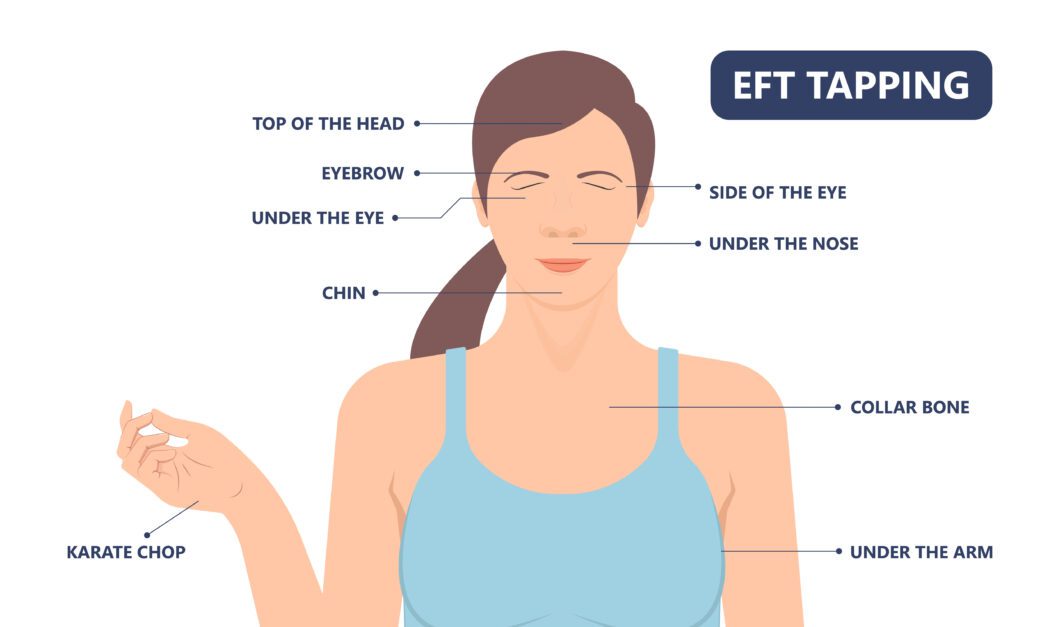
Stress is an increasingly common issue in today’s fast-paced world, affecting people across all ages and walks of life. It manifests in both physical and psychological symptoms, such as anxiety, fatigue, sleep disorders, and weakened immune function, making stress management a top priority for many individuals. Over the years, various techniques and therapies have been explored to combat stress, ranging from mindfulness and yoga to medication and cognitive-behavioural Therapy (CBT). Among these approaches is Tapping Therapy, also known as Emotional Freedom Techniques (EFT).
Tapping Therapy is a psychological acupressure technique that involves tapping on specific points on the body, primarily on the head and face, while focusing on a particular issue, such as stress or anxiety. The technique draws upon concepts from both Western psychology and Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), where tapping is believed to stimulate energy pathways, or meridians, much like acupuncture. EFT is based on the premise that negative emotions are caused by disruptions in the body’s energy system and that tapping can restore balance, reduce stress, and promote emotional well-being.
Over the last few decades, researchers have conducted various studies to evaluate the effectiveness of Tapping Therapy for stress relief This blog explores the scientific literature on Tapping Therapy, presenting key research findings, clinical trials, and expert analyses highlighting its potential benefits in stress management.
1. Understanding the Mechanism of Tapping Therapy
1) The Energy Psychology Framework
At the core of Tapping Therapy is the principle of energy psychology, which posits that emotional disturbances stem from imbalances or blockages in the body’s energy system. This is similar to the theory of meridians used in Traditional Chinese Medicine, where energy flows through specific pathways in the body. When these pathways are disrupted, individuals may experience emotional distress, pain, or illness.
In Tapping Therapy, the individual uses their fingertips to tap on specific meridian points on the body while verbalizing thoughts and emotions related to the stress they are experiencing. This combination of cognitive engagement and physical tapping is believed to release blocked energy, reducing emotional distress.
2) Connection with Acupressure and Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Tapping Therapy is sometimes compared to acupuncture, although it involves no needles. Instead, light tapping on acupressure points is employed. The practice also integrates elements of CBT, a widely recognized psychological treatment for stress, depression, and anxiety. In CBT and Tapping Therapy, patients are encouraged to confront negative emotions directly, creating an awareness of cognitive patterns while simultaneously addressing the physiological stress response.
Research Supporting the Effectiveness of Tapping Therapy
1. Clinical Trials and Meta-Analyses
One of the strongest pieces of evidence for the efficacy of Tapping Therapy in stress reduction comes from clinical trials and meta-analyses. These studies have systematically evaluated the impact of EFT on various stress-related conditions, including anxiety, PTSD (Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder), and overall psychological well-being.
2. Church et al. (2012)
A landmark randomized controlled trial by Church et al. (2012) examined the effects of EFT on the stress hormone cortisol. This study involved 83 participants divided into three groups: one receiving EFT, one undergoing supportive listening, and one control group with no intervention. The results showed a significant reduction in cortisol levels in the EFT group, with an average reduction of 24%, compared to a 14% reduction in the supportive listening group and no significant change in the control group. Lower cortisol levels indicate reduced stress, suggesting that EFT may directly affect the body’s stress response.
3. Clond (2016) Meta-Analysis
In a meta-analysis conducted by Clond (2016), the effectiveness of EFT for anxiety reduction was systematically reviewed. The study analyzed 14 randomized controlled trials with a total of 658 participants. The meta-analysis found that EFT produced a large effect size in reducing anxiety levels, with the treatment proving significantly more effective than control groups receiving no treatment or alternative interventions. The results of this analysis provide strong support for EFT as a promising intervention for anxiety-related stress.
4. Gaesser & Karan (2017)
Gaesser & Karan (2017) conducted a study focusing on college students, a population particularly susceptible to stress due to academic pressures. The research explored whether EFT could help reduce test anxiety in students. The participants who received EFT reported significantly lower test-related stress levels than those in the control group. The EFT group also demonstrated improved performance in their exams, suggesting that the technique alleviated stress and enhanced cognitive functioning under pressure.
5. EFT for Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
Many studies have examined the role of Tapping Therapy in treating PTSD, a condition often accompanied by high levels of stress and anxiety. The research into EFT’s impact on PTSD has produced promising results, suggesting that EFT can significantly alleviate symptoms of stress and trauma.
6. Church et al. (2013)
In a study by Church et al. (2013), veterans who have PTSD were provided with EFT sessions over six weeks. The results showed a remarkable decrease in PTSD symptoms in the EFT group, with 86% of participants no longer meeting the clinical criteria for PTSD after the intervention. Additionally, these participants reported lower stress levels and improved emotional well-being. The study highlights EFT’s potential as an effective therapy for individuals dealing with high levels of stress and trauma.
7. Veterans Study (2018)
Another study focusing on veterans with PTSD was conducted in 2018 and involved a larger sample size. The researchers found that the veterans who participated in EFT sessions experienced significant reductions in both PTSD symptoms and overall stress levels compared to those in the control group. The veterans continued to report improved stress management six months after the study, indicating the lasting effects of EFT on stress relief.
The Role of EFT in Reducing Physiological Stress Responses
1. Heart Rate Variability (HRV) and EFT
Heart Rate Variability (HRV) is often used as a physiological stress marker. Higher HRV is associated with a relaxed state, while lower HRV is linked to stress, anxiety, and emotional turmoil. Several studies have explored the impact of EFT on HRV as a way of measuring its physiological effects.
In a study by Baker & Siegel (2011), HRV was measured before and after EFT sessions in participants experiencing chronic stress. The results demonstrated a significant increase in HRV after the tapping sessions, indicating a shift toward a more relaxed and balanced autonomic nervous system response. This suggests that EFT helps alleviate emotional stress and has measurable effects on the body’s physiological stress markers.
2. The Amygdala and Stress
The amygdala, a brain region that processes emotions, plays a crucial role in the body’s fight-or-flight response to stress. Overactivity in the amygdala is associated with heightened stress and anxiety. Some researchers have theorized that tapping on acupressure points may help calm the amygdala, reducing the body’s stress response.
In a fMRI study by Swingle (2014), researchers measured brain activity in participants before and after EFT sessions. After the tapping therapy, the results showed a significant reduction in activity in the amygdala, suggesting that EFT can help lower the body’s physiological response to stress by calming this key brain region.
Psychological Benefits of EFT for Stress Relief
1) Improved Emotional Regulation
One key benefit of EFT is its ability to improve emotional regulation, helping individuals manage their reactions to stress. In a study by Boath et al. (2014), participants who received EFT showed enhanced emotional regulation skills, including an increased ability to remain calm in stressful situations and reduced reactivity to stressors. Improved emotional regulation can help individuals cope more effectively with stress in their daily lives, reducing the long-term impact of stress on mental health.
2) EFT and Anxiety Reduction
Anxiety is one of the most common symptoms of chronic stress. Numerous studies have shown that EFT is particularly effective in reducing anxiety levels, which in turn helps lower overall stress. A study by Sebastian & Nelms (2017) examined the effects of EFT on anxiety in individuals with high levels of stress. The researchers found that participants who underwent EFT experienced significant reductions in anxiety symptoms, with many reporting a sense of calm and emotional balance after the intervention.
EFT as a Complementary Therapy for Stress-Related Disorders
1) Integrating EFT with Traditional Therapies
While EFT is effective as a standalone therapy, it can also be used in conjunction with other treatments for stress-related disorders. For example, some clinicians have found that combining EFT with Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) can enhance the therapeutic outcomes for individuals with anxiety, depression, or trauma-related stress.
In a study by Salas et al. (2020), participants who received a combination of EFT and CBT reported greater reductions in stress and anxiety than those who received only CBT. The researchers suggest that EFT may help expedite CBT’s cognitive and emotional processing, leading to faster and more enduring results.
2) EFT for Chronic Pain and Stress Management
Chronic pain is often exacerbated by stress, leading to a vicious cycle where pain increases stress levels, and stress, in turn, heightens the perception of pain. Several studies have examined the impact of EFT on chronic pain and stress relief, with positive results.
In a study by Brattberg (2008), participants suffering from chronic pain reported significant reductions in both pain and stress after participating in EFT sessions. The results suggest that EFT can be an effective complementary therapy for individuals dealing with chronic pain, helping them manage their stress levels while also reducing the intensity of their pain.
Criticisms and Limitations of EFT Research
While the research on EFT for stress relief is promising, it is not without its critics. Some researchers have questioned the scientific rigour of certain EFT studies, particularly those that lack proper control groups or rely on self-reported data. Additionally, because EFT involves a combination of cognitive and physical components, it can be challenging to determine which aspect of the Therapy is responsible for the observed benefits.
Despite these limitations, the growing body of evidence supporting EFT’s efficacy suggests that it is a valuable tool for stress management. As more high-quality studies are conducted, the scientific community will better understand how EFT works and its long-term benefits for stress relief.
Tapping Therapy, or EFT, has emerged as a promising intervention for stress relief, with numerous studies supporting its effectiveness in reducing anxiety, PTSD symptoms, and overall stress levels. By combining cognitive focus with physical tapping on acupressure points, EFT provides a unique approach to managing stress’s emotional and physiological aspects. While more research is needed to understand the mechanisms behind EFT fully, the existing evidence suggests that it can be a valuable tool for individuals seeking to alleviate stress and improve their emotional well-being. As with any therapy, individuals interested in EFT should consult with a qualified practitioner and consider integrating it with other stress management techniques for the best results. Whether used alone or combined with traditional therapies, Tapping Therapy offers a holistic approach to reducing stress and promoting mental health.